History of the Arabian Gulf
- brender1
- Feb 21, 2016
- 3 min read
The Arabian Gulf consist of Modern day Yemen, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates (1820-1971, The Trucial States), Qatar, Kuwait, Bahrain and Oman. Each of these countries has a unique connection to Islam. These nations have been characterized by Sunni Islam, specifically the Wahhabi Movement that is derived from Saudi Arabia. Additionally, the political climate is characterized by foreign influences, such as England and the Ottoman Empire. Below is a brief summary of Arabian Gulf History, specifically the histories of Yemen, the Trucial States, and Saudi Arabia.
The Trucial States

The Trucial States were formed by the British as result of an 1820 treaty with several rulers of cities on the eastern coast of the Arabian Gulf. The Trucial States remained a protectorate of England from 1820 to 1971. For much of that period their relationship was mutually beneficial. The British protected the Trucial State against other foreign powers, such as the Ottoman Empire. Additionally, the British helped economically develop the infrastructure of the Trucial States. The Trucial States ended piracy against British naval ships, and they provided the British with strategic military bases of operation. More importantly they became a major source of oil for England. Unlike India, the leaders of the Trucial States did have significant freedom in governing their territories. Colonization in the Trucial States was not as harsh as it was in places like South America and Africa. The upsurge of Arab nationalism in Egypt in the mid-20th century rejected European colonization, specifically British rule. While Arab nationalism was prominent in other regions of the Middle East, it took almost twenty years to gain significant traction in the Trucial States.
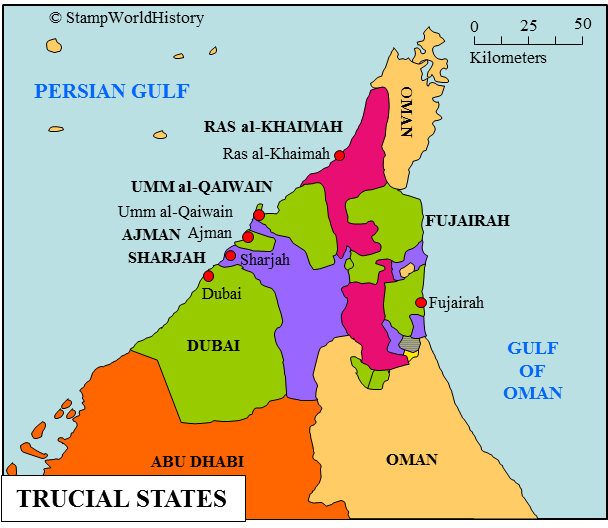
Generally, for much of their relationship with the British the leaders and people of the Trucial States were happy under British protection. Trucial State leaders, such as Sultan bin Saqr al-Qasimi of Sharja and Shaikh Ubaid bin Said al-Maktum of Dubai, were influential in convincing England to be protectors of the Trucial States. In 1892, leaders such as Saqr II bin Khalid al-Qasimi of Sharja, Sheikh Zayed I bin Khalifa Al Nahyan of Abu Dhabi, and Sheikh Humayd bin Abdullah al-Qasimi of Ras al-Khaima were instrumental in signing the 1892 treaty with the British that deepened the relationship between the British and the Trucial States. The end of the Trucial States, and the beginning of their independence as the United Arab Emirates (UAE) in 1971 was due to Arab nationalism. Many of the Trucial State leaders in the 1960s, such as Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan of Abu Dhabi, felt the pressure of Arab nationalism and saw the opportunity of independence as a way securing further power. Thus, the by the end of 1971 the British withdrew from the Trucial States, under the guise of cutting financial commitments to foreign territories. Immediately following this the former Trucial States formed what is today known as the UAE.
Saudi Arabia

The present-day Saudi Arabia owes a debt to Muhammad Ibn Saud and Muhammad Ibn Abd al-Wahhab. Both men were important in laying the foundation for Saudi Arabia’s independence. In the 18th century the Ottoman Empire held a significant influence over Saudi Arabia. Saud’s rise to power in 1744 challenged the Ottoman Empire’s dominance. Additionally, his partnership with al-Wahhab created the political-religious balance that characterizes modern Saudi Arabia. With the religious movement of Wahhabism taking center stage in the gulf region, Saudi Arabia influence grew considerably in the 19th century. Key figures such as Uthman Ibn Mu’ammar also allied with Muhammad Ibn Abd al-Wahhab. The growth of Wahhabism was a major component to the growth of Saudi Arabia.

After the Ottoman Empire was defeated in World War II, Saudi Arabia, after decades of division, united in the 1930s to become the Saudi Arabia that is known today. Like many other Arabian Gulf countries, Saudi Arabia’s oil made it a valuable partner to the West. Until the 1970’s the influence of America, and England could be seen in various degrees in the nation.
Yemen
The video below gives an excellent history of Yemen
Comments